A comprehensive solution for measuring the electrical resistivity of concrete
- Efficient all-in-one solution
- Reliable, accurate, and standardized
- Rugged waterproof construction
SPECIFICATIONS
Measured Quantity: Electrical resistivity [kΩcm]
Accuracy: From ±0.2 to ±2 kΩcm (depending on resistivity range)
Instrument Firmware: Highest resolution available for a surface resistivity instrument; Current flow indication and poor contact indication; Hold, save, and delete function
PC Software: ResipodLink to view and manipulate the data on a connected PC. It also allows a variable contact spacing to be set
Display: Pixel graphic LCD
Memory: 500 measured values
Connections: USB type B
Measuring Range: 1 to approx. 1000 kΩcm (depending on probe spacing)
Probes / Electrodes: In addition to the standard Wenner probe with spacing of 50 mm or 38 mm (1.5"), additional variable spacing probe and bulk resistivity accessories available
DOWNLOADS
Tech Specs PDF - Resipod
Resipod Family Operating Instructions
Remote Document Resipod
Resipod Family Certificates
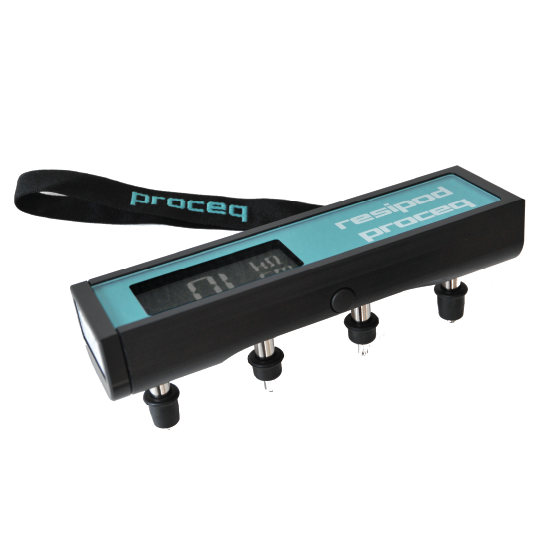

Supremely accurate concrete surface resistivity meter
Productivity
All-in-one solution for concrete electrical resistivity testing both in the lab and on-site
High Quality
Reliable, accurate, and standardized and faster than laboratory RCP testing
Reliability
Rugged, waterproof resistivity meter for use in many conditions and environments
You may also like
feedback from the field
"Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam."
"Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam."
"Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam."
Frequently Asked Questions
Do you have a NDT question that you are having a hard time getting answered? Contact GPR USA and access our experienced team of NDT professionals to get the answers you need.
FAQ One
What does electrical resistivity mean, and how do we measure it in materials?
- Electrical resistivity is a measure of a material's ability to resist the flow of electric current. It is quantified in ohm-meters (Ω·m). Resistivity can be measured using various methods, such as the four-point probe method for solids or the Wenner and Schlumberger methods for soil and concrete. These methods involve applying a known voltage across the material and measuring the resulting current to calculate resistivity.
FAQ Two
What are the main factors that influence the electrical resistivity of materials?
- Several factors can affect electrical resistivity, including temperature, moisture content, chemical composition, density, and porosity. For example, in concrete, increased moisture content typically decreases resistivity, while the presence of conductive ions (like chlorides) can significantly reduce resistivity. In metals, temperature can increase resistivity due to increased lattice vibrations.
FAQ Three
Why should we measure electrical resistivity in concrete or soil?
- Measuring electrical resistivity is crucial for assessing the durability and serviceability of concrete structures. High resistivity indicates good resistance to corrosion, while low resistivity may suggest a higher risk of corrosion of embedded steel reinforcement. In soil, resistivity measurements can help in evaluating moisture content, salinity, and the potential for ground stability issues.
FAQ Four
How can electrical resistivity be used to evaluate the corrosion risk of reinforced concrete?
- Electrical resistivity is inversely related to the likelihood of corrosion in concrete. Lower resistivity values suggest that moisture and corrosive ions can more easily penetrate the concrete, increasing the risk of corrosion of embedded rebar. By monitoring the resistivity of concrete, engineers can assess the potential for corrosion and implement preventive measures before significant damage occurs.
Resources
GPR News
connect with gpr usa today
Whether you're looking to launch a brand new company or upgrade your fleet, let GPR USA assist you every step of the way.
Product Page Contact Form
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.